vuex官网:https://v3.vuex.vuejs.org/zh/
注意版本对应
vue2要配合vuex3
vue3要配合vuex4
vuex简介
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。(说白了就是用来共享数据,可以跨组件全局共享,类似后端的session)
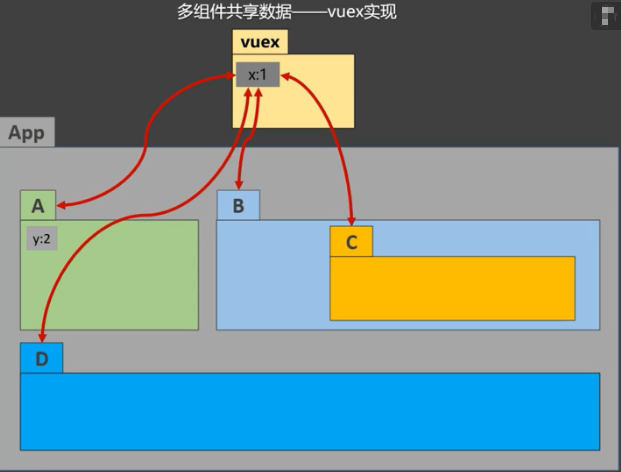
工作原理图
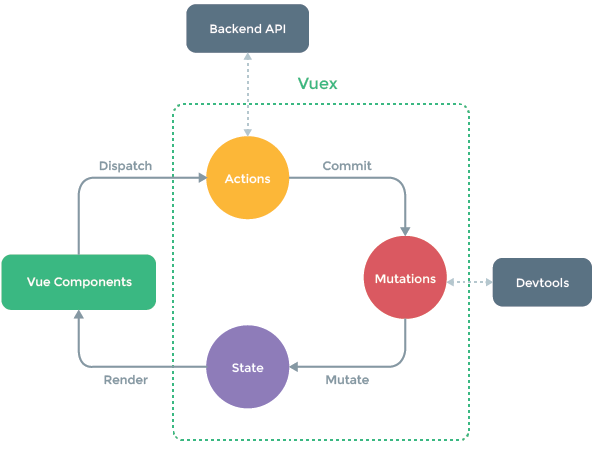
两种执行流程:
第一种(异步):vue组件—>actions—>mutations—>state
第二种:vue组件—>mutations—>state
环境搭建
使用vue cli脚手架创建即可
vuex入门案例
实现点击按钮+1的案例
- views/Count.vue 组件
<template>
<div>
<h1>Count组件</h1>
<button @click="addToVuex">vuex的count+1</button>
<!-- 模板中的this可以省略 -->
<div>vuex中的count:{{$store.state.count}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Count',
methods: {
addToVuex () {
this.$store.commit('add')
}
}
}
</script>
- store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
getters: {
},
mutations: {
add (state) {
state.count++
}
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
}
})
总结:
1>在store.js的state中设置需要共享的数据
2>在组件中通过 this.$store.state.变量名 来获取数据
3>在store.js的mutations中新增改变数据方法add
4>组件中通过 this.$store.commit(‘mutations中的方法’)来改变数据
数据存在state中,通过提交 mutation 的方式,而非直接改变
store.state.count,是因为能够更明确地追踪到状态的变化
state
Vuex 使用单一状态树,用一个对象就包含了全部的应用层级状态。这也意味着,每个应用将仅仅包含一个 store 实例。所以可以通过store来获取state中的数据
案例使用两种方式获取state中的数据
store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 2,
id: 111
}
// ...
})
this.$store.state.变量
<template>
<div>
<h1>Count组件</h1>
<!-- 模板中的this可以省略 下面两种其实是一样的-->
<div>第一种vuex中的count:{{$store.state.count}}</div>
<div>第二种vuex中的count:{{count}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Count',
computed: {
// 利用计算属性
count () {
return this.$store.state.count
}
}
}
</script>
mapState访问
<template>
<div>
<h1>Count组件</h1>
<!-- 模板中的this可以省略 -->
<div>vuex中的count:{{myCount+',id:'+myId}}</div>
<div>vuex中的count:{{count+',id:'+id}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Count',
computed: {
// myCount为自定义名称, count为vuex中state中的名称
...mapState({ myCount: 'count', myId: 'id' }),
// 当映射的计算属性的名称与 state 的子节点名称相同时,可以给 mapState 传一个字符串数组。
...mapState(['count', 'id'])
}
}
</script>
getters
Vuex 允许我们在 store 中定义“getter”(可以认为是 store 的计算属性)。就像计算属性一样,getter 的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算。
通过属性访问
- 定义store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
todos: [
{ id: 1, text: '111', done: true },
{ id: 2, text: '222', done: false },
{ id: 3, text: '333', done: true }
]
},
getters: {
// 接收一个参数
// doneTodos(state){
// return state.todos.filter(v => v.done)
// },
doneTodos: state => state.todos.filter(v => v.done),
// 接收两个参数
doneTodosCount: (state, getters) => getters.doneTodos.length
}
// ...
})
- 组件中访问
<template>
<div>
<h1>demo组件</h1>
<div>id: {{$store.getters.doneTodos[0].id}}</div>
<div>text: {{$store.getters.doneTodos[0].text}}</div>
<div>done: {{$store.getters.doneTodos[0].done}}</div>
<div>doneTodosCount: {{$store.getters.doneTodosCount}}</div>
</div>
</template>
通过方法访问
通过让 getter 返回一个函数,来实现给 getter 传参
定义store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
todos: [
{ id: 1, text: '111', done: true },
{ id: 2, text: '222', done: false },
{ id: 3, text: '333', done: true }
]
},
getters: {
// 让 getter 返回一个函数,来实现给 getter 传参
getTodoById: state => id => state.todos.find(v => v.id === id)
}
// ...
})
组件中 可以传参
<div>getTodoById: {{$store.getters.getTodoById(3).text}}</div>
mapGetters访问
mapGetters 辅助函数仅仅是将 store 中的 getter 映射到局部计算属性
和前面的mapState类似
定义store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
todos: [
{ id: 1, text: '111', done: true },
{ id: 2, text: '222', done: false },
{ id: 3, text: '333', done: true }
]
},
getters: {
// 接收一个参数
// doneTodos(state){
// return state.todos.filter(v => v.done)
// },
doneTodos: state => state.todos.filter(v => v.done),
// 接收两个参数
doneTodosCount: (state, getters) => getters.doneTodos.length,
// 让 getter 返回一个函数,来实现给 getter 传参
getTodoById: state => id => state.todos.find(v => v.id === id)
}
})
组件中
<template>
<div>
<h1>demo组件</h1>
<div>id: {{myDoneTodos[0].id}}</div>
<div>text: {{myDoneTodos[0].text}}</div>
<div>done: {{myDoneTodos[0].done}}</div>
<div>doneTodosCount: {{doneTodosCount}}</div>
<div>getTodoById: {{getTodoById(3).text}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Count',
computed: {
...mapGetters(['doneTodosCount', 'getTodoById']),
...mapGetters({ myDoneTodos: 'doneTodos' })
}
}
</script>
mutations
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation。mutation 必须是同步函数
不带参数和带参数
参数也叫载荷
store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
add (state) {
state.count++
},
// 参数也可以是对象、字符串、数组等
addN (state, p) {
state.count += p
}
}
})
组件中 通过 store.commit 方法来调用mutations中的方法
<template>
<div>
<h1>demo组件</h1>
<div>vuex中的count:{{count}}</div>
<button @click="$store.commit('add')">点击让 vuex 的count +1</button>
<button @click="$store.commit('addN',10)">点击让 vuex 的count +10</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Count',
computed: {
...mapState(['count'])
}
}
</script>
对象风格提交
store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
addNObj (state, p) {
//p就是commit提交过来的对象 {type: 'addNObj', n: 10}
state.count += p.n
}
}
//...
})
组件中
<template>
<div>
<h1>demo组件</h1>
<div>vuex中的count:{{count}}</div>
<button @click="addNObj">点击让 vuex 的count +10</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Count',
computed: {
...mapState(['count'])
},
methods: {
addNObj () {
//此处提交一个对象参数,而不是像以前那种传两个参数
//type对应mutation中的函数,n代表传来的参数,参数可以是多个
this.$store.commit({
type: 'addNObj',
n: 10
})
}
}
}
</script>
mapMutations
使用 mapMutations 辅助函数将组件中的 methods 映射为 store.commit 调用
组件
<template>
<div>
<h1>demo组件</h1>
<div>vuex中的count:{{count}}</div>
<button @click="add">点击让 vuex 的count +1</button>
<button @click="myAdd">点击让 vuex 的count +1</button>
<button @click="addN(10)">点击让 vuex 的count +10</button>
<button @click="addNObj({n: 10})">点击让 vuex 的count +10(提交对象)</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapMutations, mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Count',
computed: {
...mapState(['count'])
},
methods: {
//将 this.add() 映射为 this.$store.commit('add') ...
...mapMutations(['add', 'addN', 'addNObj']),
...mapMutations({ myAdd: 'add' })
}
}
</script>
store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
add (state) {
state.count++
},
addN (state, p) {
state.count += p
},
addNObj (state, p) {
console.log(p)
state.count += p.n
}
}
//...
})
actions
Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
- Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
- Action 可以包含任意异步操作。
分发action
Action 函数接受一个与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性的 context 对象,因此你可以调用 context.commit 提交一个 mutation,或者通过 context.state 和 context.getters 来获取 state 和 getters。
组件中可以 this.$store.dispatch(‘xxx’) 来分发
store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
add (state) {
state.count++
},
addN (state, p) {
state.count += p
},
addNObj (state, p) {
console.log(p)
state.count += p.n
}
},
actions: {
// addTimeout (context) {
addTimeout ({ commit }) {
// 执行异步操作
setTimeout(() => {
commit('add')
}, 1000)
},
addNTimeout ({ commit }, p) { //普通传参
console.log(p)
setTimeout(() => {// 执行异步操作
commit('addN', p)
}, 1000)
},
addNObjTimeout ({ commit }, p) {//对象风格传参
console.log(p)
setTimeout(() => {
commit('addNObj', p)
}, 1000)
}
}
})
组件 中 通过 this.$store.dispatch 方法触发:
<template>
<div>
<h1>demo组件</h1>
<div>vuex中的count:{{count}}</div>
<button @click="$store.dispatch('addTimeout')">点击等1秒 让 vuex 的count +1</button>
<button @click="$store.dispatch('addNTimeout',10)">点击等1秒(载荷) 让 vuex 的count +10</button>
<button @click="$store.dispatch({
type:'addNObjTimeout',
n:10
})">点击等1秒(对象风格) 让 vuex 的count +10</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Count',
computed: {
...mapState(['count'])
}
}
</script>
mapActions
使用mapActions简化上面的例子,将组件的代码改为如下
<template>
<div>
<h1>demo组件</h1>
<div>vuex中的count:{{count}}</div>
<button @click="addTimeout">点击等1秒 让 vuex 的count +1</button>
<button @click="addNTimeout(10)">点击等1秒(载荷) 让 vuex 的count +10</button>
<button @click="myAddNObjTimeout({n:10})">点击等1秒(对象) 让 vuex 的count +10</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Count',
computed: {
...mapState(['count'])
},
methods: {
//将 this.addTimeout() 映射为 this.$store.dispatch('addTimeout') ...
...mapActions(['addTimeout', 'addNTimeout']),
...mapActions({ myAddNObjTimeout: 'addNObjTimeout' })
}
}
</script>
组合action
store.dispatch 可以处理被触发的 action 的处理函数返回的 Promise,并且 store.dispatch 仍旧返回 Promise。(一个action去调用另外一个action)
组件
<template>
<div>
<h1>demo组件</h1>
<div>vuex中的count:{{count}}</div>
<button @click="addNTimeout">点击1秒后cout+1,再过1秒后count+10</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Count',
computed: {
...mapState(['count'])
},
methods: {
...mapActions(['addNTimeout'])
}
}
</script>
store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
add (state) {
state.count++
},
addN (state, p) {
state.count += p
}
},
actions: {
// addTimeout (context) {
addTimeout ({ commit }) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 执行异步操作
setTimeout(() => {
commit('add')
resolve()
}, 1000)
})
},
/* addNTimeout ({ commit, dispatch }) {
// 将addTimeout这个action组合进来
dispatch('addTimeout').then(() => {
// 执行异步操作
setTimeout(() => {
commit('addN', 10)
}, 1000)
})
}*/
//用es6的async/await来优化
async addNTimeout ({ commit, dispatch }) {
// 将addTimeout这个action组合进来
await dispatch('addTimeout')
// 执行异步操作
console.log('1010101010')
setTimeout(() => {
commit('addN', 10)
}, 1000)
}
}
})
modules
当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。
为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割
默认情况下,模块内部的 action、mutation 和 getter 是注册在全局命名空间的——这样使得多个模块能够对同一 mutation 或 action 作出响应。
如果希望你的模块具有更高的封装度和复用性,你可以通过添加 namespaced: true 的方式使其成为带命名空间的模块。
模块化语法总结:
第一: $store.commit和$store.dispatch 第一个参数为【模块名/方法命名】
例如:
$store.commit('moduleA/addN',10)
$store.dispatch('moduleA/addNTimeout',10)
第二:...mapXXX 第一个参数为模块名字符串,第二个参数和以前的写法一致
例如:
...mapState('moduleA', ['count']),
...mapState('moduleA', { moduleAcount: 'count' }),
第三:
...mapState和...mapGetters写在计算属性(computed)
...mapMutations和...mapActions写在方法里(methods)
【模块化案例】
store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 当然也可以把moduleA单独放入到一个js文件中
const moduleA = {
namespaced: true,//开启命名空间
state: {
count: 123
},
getters: {
getX2 (state) {
return state.count * 2
}
},
mutations: {
addN (state, p) {
state.count += p
}
},
actions: {
addNTimeout ({ commit }, p) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('addN', p)
}, 1000)
}
}
}
//moduleB ...
//modulec ...
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
moduleA
//moduleB ...
//modulec ...
}
})
组件中使用
<template>
<div>
<h1>模块中state的使用</h1>
<div>moduleA的count:{{ $store.state.moduleA.count }}</div>
<div>moduleA的count:{{ count }}</div>
<div>moduleA的count:{{ moduleAcount }}</div>
<h1>模块中gettters的使用</h1>
<div>moduleA的getters:{{ $store.getters['moduleA/getX2'] }}</div>
<div>moduleA的getters:{{ getX2 }}</div>
<div>moduleA的getters:{{ moduleAGetX2 }}</div>
<h1>模块中mutations的使用</h1>
<div><button @click="$store.commit('moduleA/addN',10)">moduleA的mutations+10</button></div>
<div><button @click="addN(10)">moduleA的mutations+10</button></div>
<div><button @click="moduleAAddN(10)">moduleA的mutations+10</button></div>
<h1>模块中actions的使用</h1>
<div><button @click="$store.dispatch('moduleA/addNTimeout',10)">moduleA的actions+10</button></div>
<div><button @click="addNTimeout(10)">moduleA的actions+10</button></div>
<div><button @click="moduleAAddNTimeout(10)">moduleA的actions+10</button></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Count',
computed: {
...mapState('moduleA', ['count']),
...mapState('moduleA', { moduleAcount: 'count' }),
...mapGetters('moduleA', ['getX2']),
...mapGetters('moduleA', { moduleAGetX2: 'getX2' })
},
methods: {
...mapMutations('moduleA', ['addN']),
...mapMutations('moduleA', { moduleAAddN: 'addN' }),
...mapActions('moduleA', ['addNTimeout']),
...mapActions('moduleA', { moduleAAddNTimeout: 'addNTimeout' })
}
}
</script>
vuex 持久化
vuex中数据页面刷新之后会丢失,所以可以配合cookie或localStorage来实现持久化。
这里可以使用第三方的插件vuex-persistedstate来实现
- 安装
npm install vuex-persistedstate --save
- 使用
import createPersistedState from "vuex-persistedstate"
const store =newVuex.Store({
state: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
plugins: [createPersistedState()] //使用vuex-persistedstate将数据存储到localStorage
})